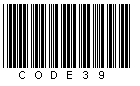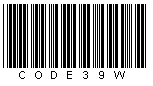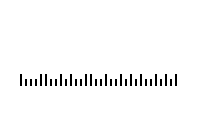Content - A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
A ^^^^^^
Resolution
Resolution is commonly used in the world of digital imaging in reference to the number of pixels within a certain area. Resolution increases as the number of pixels contained in the same areas increases.
ADF
ADF generally stands for Automatic Document Feeder. This refers to the device which, depending on the type of scanner, automatically feeds any number of sheets in a batch into the scanner one after another Just about all photocopiers these days are equipped with this device.
Auto color correction
Auto gamma correction
Gamma correction refers to the process of adjusting the background brightness of an image.
Auto contrast
This is a setting found in scanner drivers or graphics applications; it is used to automatically adjust the contrast.
Auto brightness
This is a setting found in scanner drivers or graphics applications; it is used to automatically adjust the brightness.
B ^^^^^^
Barcode
code 39
Valid characters: 0123456789[Space]ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ-.$/+%
Length: Variable (no specified length)
Check digit: Calculation according to Modulo 43
Example: Description: Code 39 is an alphanumeric code. Each character is made up of nine elements (five lines and four spaces), where three of these nine elements are wide and six are narrow. This aspect allows the self-checking of Code 39. Each character is separated by a space. The advantage of this code is the large pool of characters. The disadvantages are the low level of information density and the low tolerance.
Code 39 can be used with or without a checksum depending on the application. The checksum is calculated according to Modulo 43.
If you have a code with the text "CODE39", the barcode, without check digit, appears as below:
An alternative is the "Code 39 Checksum" type with a checksum calculation according to Modulo 43:
According to the specification, Code 39 can be created in various ratios: 2.0:1 or 3.0:1. The larger the ratio, the wider the printed barcode will be. The contents are the same, but the readability is improved.
The star is used as the start and stop character for Code 39. Usually the stars are not positioned at the beginning and the end of the plain text line. However, sometimes the "start/stop stars" are found in the plain text line; to adjust these codes, you simply must leave off the stars at the beginning and end, as the stars are a fixed component of Code 39.
code 93
Valid characters: 0123456789[Space]ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ-.$/+%
Length: Variable (no specified length)
Check digit: Calculation according to Modulo 47
Example: Description: Code 93 is an alphanumeric code, similar to Code 93, for which the character set contains the digits 0 to 9, the 26 uppercase letters (A-Z), the space character as well as special characters such as minus, period, dollar sign, forward slash, plus and percent signs.
code 128
Valid characters: Almost all ASCII characters including control characters.
Length: Variable (no specified length)
Check digit: Calculation according to Modulo 103
Example: Description: Code 128 Auto enables the display of the complete ASCII character set. To encode the alphanumeric data in the shortest possible form, there is automatic toggling between the three character sets A, B and C. Due to its high information density and the ability to display the complete ASCII character set, Code 128 has secured a large community of users.
The three character sets in detail:
These three independent character sets are only components of Code 128 and are therefore rarely used as individual types. Generally, the use of a special character set is unnecessary because the main type Code 128 automatically selects the best character set.EAN 128 or UCC 128 is a special form of Code 128. It is a logistic code for trade.
Checksum: With Code 128, a checksum is created internally that is not a part of the barcode and therefore should not be placed in the plain text line.
EAN 8
Valid characters: 0123456789
Length: 8
Check digit: Calculation according to Modulo 10
Example: Description: EAN 8 is a shorter version of EAN 13. This code is generally used for articles that do not have enough space for the EAN 13 code on the packaging. This is the case when an EAN 13 code would take up more than 25% of the front surface. An EAN 8 number is only assigned upon request because these numbers have a limited availabilty. The applicant must include with the request a sample of the article as proof of its necessity.
An EAN 8 always is composed of 8 digits:
EAN 13
Valid characters: 0123456789
Length: 13
Check digit: Calculation according to Modulo 10
Example: Description: The EAN code is mostly used in supermarkets in which the acquisition process is especially labor-intensive due to the large numbers of products per customer. The packaging of the commodities is printed with the European Article Number (EAN) or the GTIN (Global Trade Item Number), encoded as a barcode.
The standard EAN barcode has 13 digits. For smaller products there is a shorter version with eight digits, the EAN 8 code.
The EAN 13 or the GTIN is configured as follows:
The next five digits identify the manufacturer of the product. This number is assigned in Germany by GS1 Germany GmbH.
History: The EAN code was introduced in 1977 in twelve states (including all EC countries). Since then, other countries have joined in this accord, including almost all Western European countries, USA, Canada, Australia and Japan. Today, the EAN (European Article Number) is referred to as the GTIN (Global Trade Item Number).The acquisition process at the cashier in a supermarket is simplified and expedited significantly using the EAN or GTIN code. The cashier no longer is required to enter the purchase data using the keyboard on the cash register but must only guide the goods with the bar code facing downwards over the scanner. The scanner is a reading device that reads a bar code and transfers it to the computerized cash register. The computerized cash register uses the scanned product number to retrieve the corresponding product description and price from the supermarket's database.
Additional acquisition processes are no longer necessary unless a barcode is no longer readable due to external influences and must be entered manually using the keyboard. The benefits of using the EAN or GTIN codes:
Which manufacturer lies hidden behind a EAN 13 or GTIN?
Using GEPIR you can discover the manufacturer hidden in a EAN 13 or GTIN code. GEPIR is a global address database of businesses that participate in the ILN / EAN system.
GS1 DataBar Limited (formerly RSS Limited)
Valid characters: Length: Check digit: Example: Description: The former designation RSS stands for Reduced Space Symbology and has been replaced by the new designation GS1 DataBar.
GS1 DataBar Limited was developed to identify very small products that cannot be captured in an omnidirectional environment. It can encode a 12, 13 or 14-digit GTIN, whereas the indicator in a 14-digit GTIN can only accept the value 1.
A 14-digit GTIN with an indicator higher than 1 must use a different barcode symbol from the GS1 DataBar family.GS1 DataBar Omnidirectional (formally RSS 14)
Valid characters: Length: Check digit: Example: Description: The former designation RSS stands for Reduced Space Symbology and has been replaced by the new designation GS1 DataBar.
GS1 DataBar Omnidirectional uses the Application Identifier AI (01) to encode the GTIN in a linear symbol that can be read omnidirectionally (regardless of position and orientation) by every standard slot scanner.
Intelligent Mail
Valid characters: Length: 65 Check digit: Example: Description: The Intelligent Mail barcode is a 65-barcode for use on mail in the United States. The hope is that the additional information in the bar code will provide benefits to both customers and postal officials.
The Intelligent Mail initiative was created by the US Postal Service in 2003, became available in 2006, and was expanded in 2007. This barcode should be fully operational as of fall 2009. The participating companies expect to benefit from the increased automation in the US Postal Service.
The Intelligent Mail barcode replaces POSTNET and PLANET barcodes and promises to provide improved customer service and efficiency.
The Intelligent Mail barcode also is referred to as OneCode, IMB and the 4-State barcode.
Allocation of the elements:
Example: 05,987,978425,684745129,92130
The text can be located below or above the barcode in accordance to the specifications.
Interleaved 2 of 5
Valid characters: 0123456789
Length: Variable (no specified length)
Check digit: >Calculation according to Modulo 10
The checksum is optional. The original version of this code did not use a checksum.
Example: Description: The 2 of 5 Interleaved code is a numeric code. Its character set contains only the digits 0 to 9. It is a version of Code 25.
The goal is to save space by displaying in pairs the digits to be encoded. The code is composed of two wide and three narrow lines or two wide and three narrow spaces. Two digits always form a pair. The first digit is composed of five lines, the second digit then is composed of the spaces that come directly after the first digit. The pair of digits is displayed by five lines and spaces.
An example for the difference between Code 25 Industrial and Code 25 Interleaved: The digits 123456 will be encoded. The result as Code 25 is as follows:
In comparison, the digits 123456 encoded as Code 25 Interleaved:
Code 25 Interleaved does not have a built-in check digit. However, it does offer the advantage of being self-checking, similar to Code 39, as well as a high information density that requires little space. The low tolerance as well as the paired display of the characters could be considered disadvantages. If an uneven number of characters needs to be displayed, a zero must be placed at the beginning of the code (123 would be 0123) or a self-created check digit is added at the end.
ITF-14
Valid characters: 0123456789
Length: 14
Check digit: Calculation according to Modulo 10
Example: Description: The ITF-14 bar code (also called SCC-14) is used to create the Shipping Container Symbol. This code is used to identify cartons and palettes that contain goods marked with an EAN-13 code. One digit is added in front of the EAN-13 code to identify the type of packaging.
The ITF-14 code is always 14 characters long:
The name ITF-14 designates the type of barcode used, Interleaved 2 of 5 (Code 25 Interleaved, ITF = Interleaved Two of Five) and the 14 digits that are displayed, the length of the container symbol.
The ITF-14 bar code itself can have a thick, solid frame around the barcode. The lines forming the frame are called bearer bars. This frame is not required for recognizing this barcode.
Patch code
Valid characters: Only predefined types are possible
- Patch 1
- Patch 2
- Patch 3
- Patch 4 (Toggle patch)
- Patch 6
- Patch T (Transfer patch)
Length: - Check digit: -
Example: Description: Patch codes are generally used to separate documents or to control a scanner automatically. For example, with certain scanner models a patch code can be used to switch from simplex to duplex or to control a counter. Planet
Valid characters: 0123456789 Length: 12 or 14 characters Check digit: yes
Example: Description: The Planet barcode is used by the U.S. Postal Service. The barcode consists of:
- Two digit service type ID
- Five digit subscriber ID
- Four or six digits are for the user's own purposes
- Check digit:
Plus 2
Valid characters: Length: Check digit: Example: Description: The plus 2 code always is used in connection with a basic code and can be considered an extension. Here is the EAN-8 + 2 digits.
The extension is used for printed materials that recur monthly and identifies the calendar week (01 - 52) or the month (01 - 12) they recur.
The additional code is widely used globally.Plus 5
Valid characters: Length: Check digit: Example: Description: The plus 5 code always is used in connection with a basic code and can be considered an extension. Here is the EAN-8 + 5 digits.
The extension is used for printed materials such as journals, newspapers and books. The additional characters identify the day or the price of the item.
The additional code is widely used globally.Postnet
Valid characters: 0123456789 Length: Variable (no specified length) Check digit: Calculation according to (see below)
Example: Description: PostNet (Postal Numeric Encoding Technique) is a code used by the U.S. Post Office. It is used to reproduce the zip code of the addressee in a machine-readable format. This expedites the sorting of mail so the addressee receives the mail more quickly.
The PostNet barcode consists of the following elements:
The checksum is calculated by first adding together all the digit encoding data. The difference of this sum from the next number that is divisible by 10 is the checksum.
There are three variations of the PostNet bar code that are used most frequently. They differ in the length of the encoded data:
RM4SCC (Royal Mail)
Valid characters: 01234567890ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ Length: Variable (no specified length) Check digit: none
Example: Description: Royal Mail 4 State Customer Code (RM4SCC) was developed for the automatic sorting of mail. Normally, this code is used to encode the ZIP code and the house or P.O. Box number and reproduce it in a machine-readable format. The contents of this code varies from country to country.
Telepen
Valid characters: Complete ASCII character set Length: Check digit: Example: Description: Telepen can be used to represent the full range of ASCII characters. This covers the standard set of printable characters including numbers, upper and lowercase letters and punctuation marks as well as the complete set of non-printable control characters such as carriage return, line feed, horizontal tab, etc.
Telepen can also be used to represent numeric data in double-density mode, where an ASCII character is re-interpreted as a pair of numeric characters. There is nothing in the barcode to distinguish between the two modes, and the interpretation of the data as ASCII or numeric is determined only by the configuration of the reading device.
Telepen systems have been implemented in many countries and very widely in the U.K. Most universities and other academic libraries use Telepen, as do many public libraries. Other users include the motor industry, Ministry of Defense and innumerable well-known organizations for many different applications.
UPC-A
Valid characters: 0123456789 Length: 12 Check digit: Calculation according to Modulo 10
Example: Description: The UPC A code is the normal 12-digit version of the UPC code and is similar to the EAN code. It also is called UPC 12. The UPC code is a numeric code that represents the digits 0-9. Each character comprises two lines and two spaces.
The UPC A code consists of the following elements:
0 - Regular UPC code
1 - Reserved (possibly for later use)
2 - Products sold by weight. This code is created at the store to mark products.
3 - National Drug Code (NDC) and National Health Related Items Code (HRI)
4 - UPC code that can be used without any format restrictions
5 - Coupon
6 - Regular UPC code
7 - Regular UPC code
8 - Reserved for later use
9 - Reserved for later use
UPC-E
Valid characters: 0123456789 Length: 8 Check digit: Calculation according to Modulo 10
Example: Description: The UPC code is a shorter version of the UPC code that is a numeric code with the digits 0-9.
The UPC E has 8 digits, whereby the eighth digit is the check digit and the first one is a system identifier, which is always a "0". The encoded digits are included as plain text under the code.
DataMatrix
Valid characters: Length: Check digit: Example: Description: DataMatrix is a two-dimensional (2D) barcode symbology which can store from 1 to about 2,000 characters.
DataMatrix ECC200 version supports advanced encoding error checking and correction algorithms (Reed-Solomon). Those algorithms allow the recognition of bar codes that are up to 60% damaged.
DataMatrix is being used to encode product and serial number information on electrical rating plates, to mark surgical instruments in Japan, and to identify lenses, circuit boards and other items during manufacturing.
Barcode Professional supports all DataMatrix Formats and the data represented in the symbol can be compressed using one of following algorithms:
- ASCII: is used to encode data that contains mainly ASCII characters (0-127).
- C40: is used to encode data that contains mainly numeric and uppercase characters.
- Text: is used to encode data that contains mainly numeric and lowercase characters.
- Base256: is used to encode 8 bit values.
Micro QR
Valid characters: Length: Check digit: Example: Description: Micro QR stands for Micro Quick Response Code.
The image shows the code produced by the representation of the string:
ABC123456789
QR Code is a kind of 2D (two-dimensional) symbology developed by Denso Wave (a division of Denso Corporation at the time) and released in 1994 with the primary aim of being a symbol that is easily interpreted by scanner equipment. Micro QR Code is a very small QR Code barcode that fits applications requiring a smaller space and using smaller amounts of data, such as the identification of printed circuit boards and electronics parts, etc.Micro QR Code is capable of handling all types of data, such as numeric and alphabetic characters, Kanji, Kana, Hiragana, symbols, binary and control codes.
The symbol versions of Micro QR Code range from Version M1 to Version M4. Each version has a different module configuration or number of modules (the module refers to the black and white dots that make up the Micro QR Code). Module configuration refers to the number of modules contained in a symbol, commencing with Version 1 (11 x 11 modules) up to Version 4 (17 x 17 modules). Each higher version number comprises two additional modules per side. Each Micro QR Code symbol version has the maximum data capacity according to the amount of data, character type and error correction level.
Micro QR Code is not capable of storing much data (maximum 35 numeric characters). However, because it can store data for each symbol size more efficiently than QR Code, the size of Micro QR Code symbols does not significantly increase, even though the amount of data is increased.
PDF417
Valid characters: Length: Check digit: Example: Description: PDF417, or Portable Data File 417, is a two-dimensional (2D) stacked barcode symbology capable of encoding over a kilobyte of data per label. It was developed by Symbol Technologies (1989-1992) and is currently maintained by ISO/IEC.
Large amounts of text and data can be stored securely and inexpensively using the PDF417 symbology. The printed symbol consists of several linear rows of stacked codewords. Each codeword represents 1 of 929 possible values from one of three different clusters. A different cluster is chosen for each row, repeating after every three rows.
The data is encoded using one of three compaction modes: text compaction mode, binary compaction mode, and numeric compaction mode.
Barcode Professional products support the following PDF417 compaction modes:
Text: allows the encoding of all printable ASCII characters, i.e. values from 32 to 126 inclusive in accordance with ISO/IEC 646, as well as selected control characters such as TAB (horizontal tab ASCII 9), LF (NL line feed, new line ASCII 10) and CR (carriage return ASCII 13).
Binary: enables the encoding of all 256 possible 8-bit byte values (ISO/IEC 8859-1). This includes all ASCII characters value from 0 to 127 inclusive and provides for international character set support.
Numeric: Enables the efficient encoding of numeric data strings.
Auto: Switches between Text, Binary and Numeric modes in order to minimize the number of codewords to be encoded.
PDF417 Error Correction Level
PDF417 uses Reed Solomon error correction instead of check digits. This error correction allows the symbol to withstand some damage without causing loss of data. The error correction levels range from 0 to 8. The recommend minimum error correction level is 2.
Compact PDF417
Barcode Professional products support the Compact PDF417 (formerly Truncated PDF417) version which omits the right-hand portion (right row indicator stop pattern) in order to save space. Please refer to Compact PDF417 Symbology for further details.
QR code
Valid characters: Length: Check digit: Example: Description: This image shows a code that results from the representation of the string:
ABC 123456789
QR Code is a kind of 2D (two-dimensional) symbology developed by Denso Wave (a division of Denso Corporation at the time) and released in 1994 with the primary aim of being a symbol that is easily interpreted by scanner equipment.
QR Code is capable of handling all types of data, such as numeric and alphabetic characters, Kanji, Kana, Hiragana, symbols, binary and control codes.
The symbol versions of QR Code range from Version 1 to Version 40. Each version has a different module configuration or number of modules (the module refers to the black and white dots that make up QR Code). Module configuration refers to the number of modules contained in a symbol, commencing with Version 1 (21 x 21 modules) up to Version 40 (177 x 177 modules). Each higher version number comprises four additional modules per side. Each QR Code symbol version has the maximum data capacity according to the amount of data, character type and error correction level. In other words, as the amount of data increases, more modules are required to create the QR Code, resulting in larger QR Code symbols.
QR Code has error correction capability to restore data if the code is dirty or damaged. Four error correction levels are available for users to choose from according to the operating environment. Raising this level improves error correction capability but also increases the size of the QR Code. To select the error correction level, various factors such as the operating environment and QR Code size need to be considered. Level Q or H may be selected for a factory environment where the QR Code might get dirty, whereas Level L may be selected for clean environments with a large amount of data. Typically, Level M (15%) is the most frequently selected. The QR Code error correction feature is implemented by adding a Reed-Solomon code to the original data.
Batch scan
In scanners with ADF, this is the mode of operation for automatic processing of a batch of paper lying in the ADF.
Document width
The document width is given as the maximum and minimum values permissible. If this value is exceeded, paper jams will occur in the scanner. Widths falling short of this value will either cause paper to jam or distortions to appear in the scan result as the original cannot be kept secure while scanning, causing its orientation to change as it passes through the scanner.
Exposure
A setting to be made mostly for non-contact scanners. In order to compensate for changes in the ambient light and differences in lightness in the original, many book scanners perform a prescan to get a rough sample of the original and determine the right exposure.
Bitonal
A black and white image is called bitonal because it only contains pixels of those two conditions (tones).
Book scanner
A non-contact scanner or scanner with a pane of glass to press the original flat, used to gather information from books. High quality book scanners do not require a pane of glass to press the pages flat as they are equipped with integrated book-fold correction. Before information is gathered, it records the distortion of the pages in the book and adjusts the focus while scanning so as to produce a consistenly sharp image at the end.
C ^^^^^^
CCD
CCD stands for charge coupled device. One-dimensional CCDs are usually used in scanners. This optical component serves to capture information in an image. Depending on how the scanner is built, the CCD is either guided over the document or vice-versa. In flatbed scanners, the CCD normally runs beneath the document, while in high-volume mass document scanners the document is guided past the CCD.
Contrast
(Übersetzung von Kontrast hier einfügen)
D ^^^^^^
Density
(Übersetzung von Dichte hier einfügen)
Dichte
Typically describes the transparency of a material. The density of the printed image in a document is also described using this term. Where density is poor, image information is either ridden with errors or is highly/roughly pixelated.
DMS
Stands for document management system. This system serves to file large amounts of records and make them easy to use for research purposes using full text search. A typical example of its use would be in a housing association, where a great deal of correspondence is exchanged with tenants.
Document scanner
In contrast to flatbed scanners, the emphasis here is on throughput. Quality only plays a role in terms of the readability of the information. For projects with a mixture of documents, color pages are usually captured using a different scanner and then reintegrated into the batch using software.
Double sheet monitoring
A device that prevents and detects when multiple sheets of paper are fed. See multiple sheet-feed.
Duplex
Refers to capturing both the front and rear page of a document simultaneously.
E ^^^^^^
Endorser
A device that prints a user-defined string onto the documents being scanned.
Feed roller
The most crucial component in scanners with ADF for paper feed. Excessive use or a hardening of this roller will inevitably lead to feed problems.
F ^^^^^^
Color depth
Indicates the depth at which a pixel can be graded for color display. The color depth of black and white images is of course 2, for grayscale images it is usually 8 bit, which means 256 colors are defined, and for color images it can be up to 48 bit depending on the image.
Flatbed scanner
Flatbed scanners, which are widely used for personal use, are typically not designed for large volumes. They are designed more for high quality scans.
Photo
A filter is normally hidden behind this function, which takes the conditions particular to real photographs into consideration while scanning.
G ^^^^^^
Gamma correction
Gamma value
Speed
Grayscale
Typically refers to a category of image that displays image information purely in various grades of gray ranging from black to white. Up to 256 grades are possible.
H ^^^^^^
Brightness
The term brightness describes the background brightness of a scanned image. As the brightness scale is slid up to higher values, the image generally becomes brighter. This is useful when information disappears into darkness in parts of the scanned image, but the information can clearly be made out in the original. If the digital image is overexposed, or too bright, the scale can be moved towards the darker direction to make information readable if necessary.
High gloss
Is a filter function that aims to compensate for conditions particular to high gloss originals.
Portrait
The shorter side of a DIN-A* sheet is defined as portrait when horizontal, or perpendicular to the scanning direction. You should only scan your originals in portrait format if the maximum document width of the scanner would be exceeded in landscape format.
I ^^^^^^
Invert
This function calculates the reciprocal value of each pixel, causing the image to be displayed inverted. This function is often necessary in microfilm scanners as film is usually exposed as a negative and the image information is meant to be inverted.
J ^^^^^^
Job
The working unit of a scanner, or final structure of a scanning project.
K ^^^^^^
Contrast
The contrast controls the increments of information within a digital image. As the contrast is adjusted higher, the image becomes increasingly closer to being displayed in black and white.
L ^^^^^^
Length correction
M ^^^^^^
Multiple sheet-feed
Describes the undesired effect of multiple documents being fed at once. This is a dreaded error for which much effort is made to prevent if possible. The information relevance of this error is the reason. As a result, whole pages often just "disappear" from a scanning project. Various methods are employed to detect multiple sheet-feed. One of these is monitoring the length of documents. Sheets fed in multiple are rarely in line with each other, and so a document length differing greatly from the average results. This can be used as a criterium for error detection. Another method is applying low-pressure suction to both sides of the document. A single sheet does not allow the suction cups to separate, while this separation is immediately apparent with two or more sheets; this is therefore a criterium to use for error detection. Ultrasonic sensors are being used more and more frequently. The risk of multiple sheets being fed increases as the physical condition of the documents worsens.
N ^^^^^^
O ^^^^^^
Original
A commonly used term for the document being captured by the scanner to create a digital reproduction.
P ^^^^^^
Paper feed
The mechanism in a scanner that moves the documents through the scanner.
Pixel
A single point, or dot, in an image. Thus at a resolution of 300 DPI (dots per inch), 300 points or dots are contained within an inch, or 2.54 centimeters. If we divide 2.54 cm by 300, we effectively get a pixel width of about 84 µm, or 0.084 mm. It is quite clear that the human eye is not able to detect a pixel of this size; therefore, a constellation of many pixels creates an image.
Q ^^^^^^
Landscape
The longer side of a DIN-A* sheet is defined as landscape when horizontal, or perpendicular to the scanning direction. If you have access to a high performance computer, it might be faster if you scan documents in landscape format and automatically rotate the images later using scan software.
R ^^^^^^
Rear page
In duplex scanners, this is usually the side turned away from you, or back page. In cases where important information is contained on the rear page both pages are captured.
Bitmapped graphic
Is typically a filter function in scanners. Moiré patterns tend to turn up when bitmapped graphics are scanned. This filter serves to minimize this effect.
S ^^^^^^
Scan width
The value of the maximum width of a document possible, normally given in cm, which will not get stuck in the scanner chamber. Paper jams are normally the result if attention is not paid to this value.
Scan length
Refers to the length of a document which the scanner can translate into an image. This value typically depends on the memory of the scanner and the intended use of the scanner.
Simplex
Batch
Usually refers to a unit of organization in DMS based filing of documents.
Batch scanning
In scanners with ADF, this is the mode of operation for automatic processing of a batch of paper lying in the ADF.
Black and White (B/W)
Another term for bitonal. Black and white images are basically composed of pixels which are either black or white. Intermediary tones cannot be displayed. The bitmapped graphic is a special type of such an image. By cleverly arranging black or white pixels, the impression of gray scales is created for the human eye.
T ^^^^^^
Text mode
A common term for the normal mode, especially in book scanners. Alternatively, a photo or grayscale mode is also usually available.
Driver
A term for the software that establishes a connection between the scanner and the operating system or scanning application. We have decided to include just a basic glossary in this manual. Due to the wide variety of scanners available on the market, it would be impossible to include a more detailed explanation. Scanner manufacturers normally include a detailed help file with their product.
U ^^^^^^
Envelope
A standard format in the document size settings supplemented by the fitting standard envelope size.
V ^^^^^^
Document size
May either be a standard DIN-A* size or user-defined dimensions. Most scanner drivers do not permit any settings beyond the maximum scan width, and they will automatically change the value to the maximum allowed.
Original
The original document from which the scanner creates a digital reproduction.
W ^^^^^^
Roller
This term is usually encountered in scanners in connection with errors. For example, if the scanner repeatedly detects problems with the paper feed, it might display the following message: Please clean feed roller.
X ^^^^^^
X coordinate
Y ^^^^^^
Y coordinate
Z ^^^^^^
Zoom